Vibration Monitoring and Reports are crucial aspects of managing and mitigating the effects of vibrations in various industries, such as construction, mining, manufacturing, and civil engineering. Monitoring vibrations helps ensure that operations do not exceed safe limits and minimizes potential damage to structures and infrastructure. Here’s a comprehensive look at vibration monitoring and reporting:
1. Vibration Monitoring
a. Objectives of Vibration Monitoring
- Safety: Ensure that vibrations do not exceed levels that could harm people or cause structural damage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet local, national, or international standards and regulations regarding vibration limits.
- Structural Integrity: Protect buildings, roads, and other infrastructure from vibration-induced damage.
- Operational Efficiency: Optimize operations to minimize vibration impacts and improve performance.
Types of Vibration Monitoring
Environmental Vibration Monitoring:
- Purpose: Measure vibrations caused by external factors such as traffic, construction activities, or industrial operations.
- Devices: Seismometers and accelerometers placed at various locations to capture ambient vibrations.
Operational Vibration Monitoring:
- Purpose: Monitor vibrations generated by machinery and equipment to ensure they are operating within safe limits.
- Devices: Vibration sensors and accelerometers attached to machinery to monitor vibration levels.
Structural Vibration Monitoring:
- Purpose: Assess vibrations transmitted to structures, such as buildings and bridges, to detect potential damage.
- Devices: Vibration sensors and strain gauges mounted on or near the structure.
Vibration Reports
a. Contents of Vibration Reports
Introduction:
- Purpose: Explanation of the monitoring objectives and scope.
- Site Description: Overview of the monitored location, including relevant details about nearby structures or sensitive areas.
Monitoring Equipment:
- Details: Information about the types of sensors used, their locations, and calibration details.
Data Presentation:
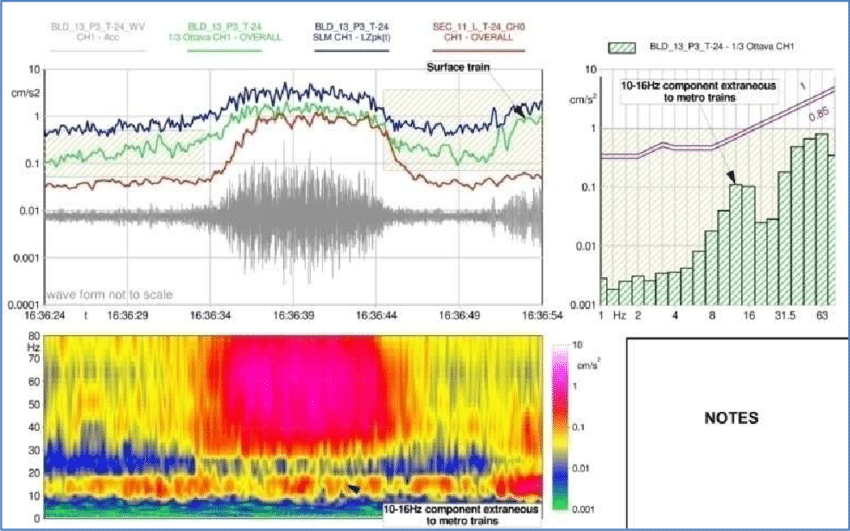
- Vibration Levels: Presentation of measured vibration levels in terms of acceleration, velocity, or displacement.
- Time-Series Data: Graphs and charts showing vibration levels over time.
- Frequency Analysis: Analysis of vibration frequencies and identification of dominant frequencies.
Compliance and Standards:
- Comparison: Assessment of vibration levels against regulatory limits and industry standards.
- Compliance Status: Indication of whether the measured levels are within acceptable ranges.
